
Questions about scaffolding – what you need to know
How do you secure scaffolding?
Scaffolding must be secured with guardrails and kick boards (toe boards) in each bay to prevent people or objects from falling. If the scaffolding is more than 30 cm from the wall, there must also be guardrails and kick boards on the inside of the scaffolding.
How do I know which type of scaffolding to choose?
The scaffolding design depends on the type of work to be carried out. For example, for simple facade work or light timber work, there is no need for scaffolding that can withstand large loads; a class 3 facade scaffold (200 kg/m² evenly distributed load) will be sufficient. If there is a need to temporarily store heavier materials such as bricks, a heavy duty scaffold is required. This can withstand loads up to class 6 (600 kg/m² evenly distributed load).
How far can the scaffolding stand from the wall?
The scaffolding floors must be installed so that the individual components cannot move during normal use. The unsecured distance between the scaffolding and the wall must not exceed 0.30 metres. If the gap between the scaffolding and the wall exceeds 30cm, the railing and toe board must also be installed here.
When is there a requirement for guardrails on scaffolding?
Scaffolding floors or stairs that are higher than 2.0 metres above the ground must always have guardrails. If there are special hazards in the event of a person or object falling from the scaffolding floor, the scaffolding or access must have guardrails, even at lower heights.
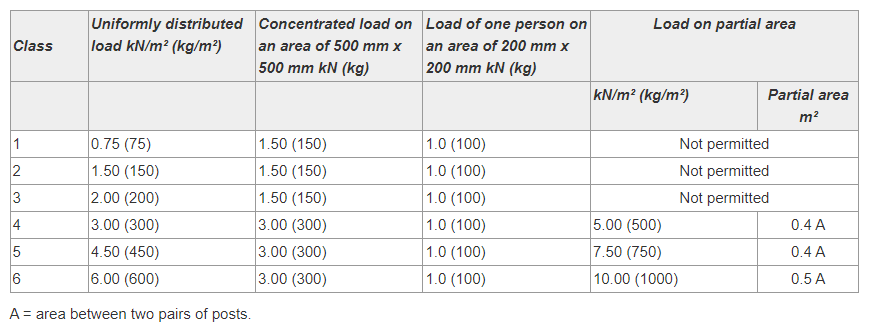
What load classes are there for scaffolding?
Scaffolding is divided into six classifications:
Class 1 – 75 kg/m²: Lowest load capacity, suitable for inspections and light maintenance work.
Class 2 – 150 kg/m²: This class is suitable for light maintenance work, such as painting.
Class 3 – 200 kg/m²: Intermediate class designed for general building work carried out by craftsmen.
Class 4 – 300 kg/m²: Ideal for masonry work requiring both equipment and storage of bricks (distributed evenly).
Class 5 – 450 kg/m²: Intended for heavier masonry work involving the storage of equipment and cubic pallets.
Class 6 – 600 kg/m²: The heaviest class, intended for heavy masonry work.
How do you anchor the scaffolding?
The scaffolding must be anchored continuously during assembly with wall brackets. As a general rule, all frames should be secured on every other floor, as well as the top floor level. It should be noted that extra anchoring is required when using scaffolding net, tarpaulin or winch.
What are the training requirements for the use and installation of scaffolding?
Sections 17-2 to 17-5 of the Regulations on the performance of work stipulate training requirements for different scaffolding heights:
2-5 metres: 7.5 hours theory and 7.5 hours practice.
2-9 metres: 15 hours theory and 15 hours practice.
Over 9 metres: 36 hours theory, 72 hours practice on 3 different types of scaffolding + employment for at least 6 months in a company that uses scaffolding.
Users must also be trained in the use of the scaffolding in question, including reviewing instructions for assembly, use and dismantling.
Who can inspect and approve scaffolding?
Before use, the scaffolding must be inspected and checked by a qualified person. An employee who has undergone training in accordance with the regulations is considered qualified. For example, an employee who has completed training in accordance with section 17-2 of the regulations is considered qualified for scaffolding with an upper scaffold floor of up to five metres. The scaffolding must be inspected regularly as long as it is in use. It must always be inspected after storms, in the event of conditions that may have affected stability and strength, and if the scaffolding has not been used for a week or more.
Is fall protection required for scaffolders?
Yes – the rules require all scaffolders to be trained in the use of fall protection equipment. The regulations clearly state that all scaffolders must be given “training in the use of relevant safety equipment that can protect against falls during the assembly, dismantling and modification of scaffolding structures” (see Regulations on the performance of work, new sections 17-2, 17-3 and 17-4). This means that all scaffolders must be trained in the use of fall protection equipment.
From what height do you need a scaffolding course?
The rules state that anyone installing scaffolding above a platform height of 2 metres must have documented training.
What are the requirements for scaffolding courses for private individuals?
There are strict regulations for working at height, and it is the Norwegian Labour Inspection Authority that regulates this in Norway. These regulations apply to professionals working at height, but they are not as strict for private individuals. On a general basis, it can be said that private individuals who are going to use the scaffolding on their own do not need a scaffolding course (NB: when the scaffolding is for their own use). It is important that the supplier’s user guide is carefully followed. As a private individual, you may have employer responsibility – so it is important to be aware of your own role and responsibilities.
How do I secure scaffolding with guardrails on a sloping roof?
Work above 2 metres must always be secured with guardrails. The guardrail must be a minimum of 1.0 metre, with handrail, knee rail and foot rail. The railing must be able to withstand the greatest calculated load in the event of a fall. When working on roofs with a steep slope and/or roofs with a large distance to the eaves, it should also be considered whether personal fall protection equipment should be used in addition to guardrails or scaffolding.
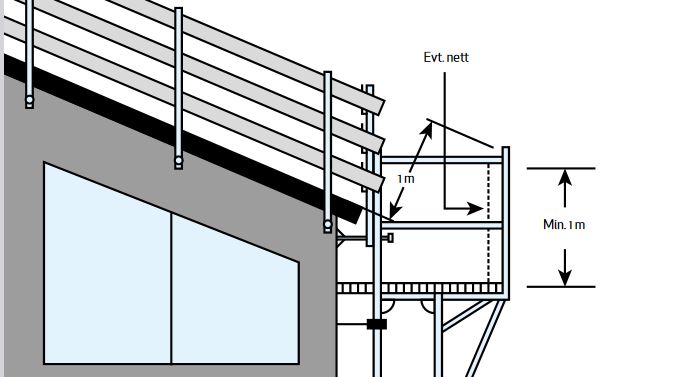
Is it permitted to work on roofs without safety equipment?
No – When working on roofs where there is a risk of falling, employees must always be secured against falling. Collective safety measures, such as railings or scaffolding, must be used. When working on roofs with a steep slope and/or roofs with a large distance to the eaves, it should also be considered whether personal fall protection equipment should be used in addition to guardrails or scaffolding.
What are the requirements for scaffolding certification?
Scaffolding sold in Norway must have a product certificate. This certificate must be issued by an accredited certification body within the EEA, where the certification body must be accredited for the task. This is a quality mark from an independent third party that the product fulfils the requirements of the manufacturer regulations and relevant product standards. The certificate shows, among other things, the load class and that the product has been strength-calculated and passed testing. This provides predictability and security for the end user.
How is the height of the scaffolding calculated?
The platform height is calculated from the ground to the platform.
The scaffolding height is calculated from the ground to the top railing (usually platform height + 1m).
The working height is calculated from the ground to the point a person can reach from the top level (usually platform height + 2m).
What do the regulations say about the inspection of scaffolding?
As long as it is in use, scaffolding must be inspected at regular intervals depending on the conditions. After a storm, when other conditions may have affected stability and strength, and when the scaffolding has been out of use for a week or more, the scaffolding must be checked before it is put into use.
What are the requirements for scaffolding signage?
All scaffolding must have an easily visible sign (also known as an approval card) showing whether the scaffolding is approved or not approved for use. The sign must be legible and able to withstand weather and wind over time. The sign must be updated after each inspection.




